XXVI, Issue 2, May 2022
Page 10
Previous Page
Next Page
SOME HEALTH & SCIENCE NEWS

"Got Milk?" 1974 - Blush
1. Bartonella Bacteria Found in Hemangiosarcoma Tumors from Dogs
2. As marijuana is becoming legal in more and more states, cases of pets becoming poisoned are on the rise too.
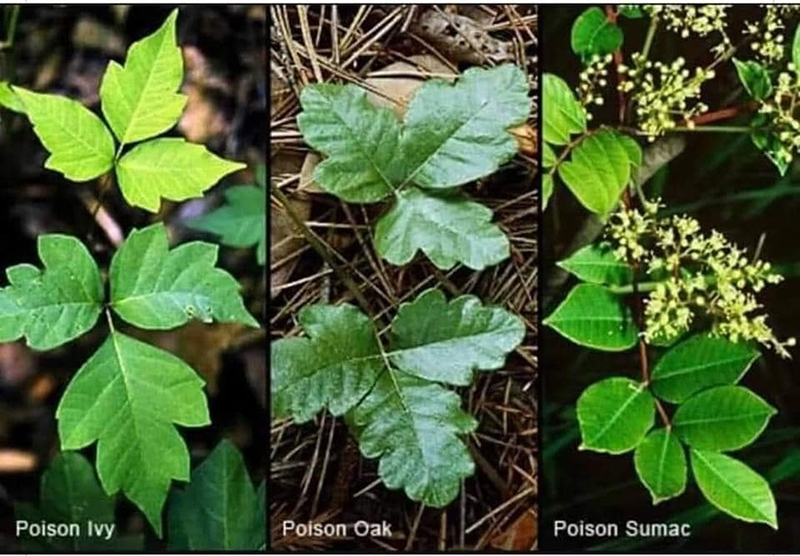
3. Poison Ivy Images.
Bartonella Bacteria Found in Hemangiosarcoma Tumors from Dogs.
Researchers from North Carolina State University have found a very high prevalence of Bartonella bacteria in tumors and tissues – but not blood samples – taken from dogs with hemangiosarcoma, a cancer of the blood vessels. The work further supports the connection between persistent infection and some types of cancer and adds to the evidence that Bartonella can remain and thrive, undetected, within tissue.
Hemangiosarcoma (HSA) is an aggressive, deadly cancer that arises from cells lining the blood vessels. It is responsible for two-thirds of all heart or splenic tumors in dogs, and is most common in medium-sized and middle-aged dogs. Since HSA usually cannot be diagnosed without major abdominal surgery, most HSA remains undetected until it has reached an advanced stage, resulting in a one-year survival rate of only 12 to 20%.
“There are clear precedents for the involvement of bacterial infections in tumor development,” says Ed Breitschwerdt, Melanie S. Steele Distinguished Professor of Medicine at NC State’s College of Veterinary Medicine and corresponding author of a paper describing the work. “Given the established links between chronic inflammation and cancer, we wanted to determine whether chronic infection of blood vessels due to bacteria could be a contributing cause of this cancer.”
Breitschwerdt and colleagues from NC State looked at tumor tissue, non-tumor tissue and blood samples from 110 dogs with HSA from across the U.S. They screened both the tissues and the blood for Bartonella, Babesia, and Mycoplasma, three bacteria associated specifically with blood infections.
Bartonella DNA was amplified and sequenced from 80 of the dogs with HSA: it was present in 34% of tumor tissue and 63% of non-tumor tissue, but appeared in none of the blood samples. Mycoplasma DNA was only amplified from 5 of the dogs and Babesia wasn’t detected in any dog.
“Research in recent years has confirmed that persistent infection with or inflammation caused by stealth pathogens is a risk factor for developing cancer later in life,” Breitschwerdt says. “With the exception of Helicobacter pylori, the emphasis on evaluating the relationship between infection and cancer has focused on viruses. But intracellular bacterial pathogens such as Bartonella may also play an important and previously uninvestigated role.
“Bartonella is a stealth pathogen – it can ‘hide’ in the cells that line blood vessel walls, which is part of what makes it so difficult to detect,” Breitschwerdt says. “This work adds more evidence to the connection between infection and cancer risk, and demonstrates that molecular testing of whole blood samples does not rule out the tissue presence of this pathogen. Future studies are needed to investigate whether Bartonella infection can be a cause of HSA. Our team will be focusing on creating more sensitive diagnostic testing as part of this effort.”
The work appears in PLOS ONE and was supported by the American Kennel Club Canine Health Foundation (Grant 2550) and the Comparative Medicine and Translational Research Program of the National Institutes of Health (T32OD011130). Ph.D. student Erin Lashnits is first author.
~Tracey Peake/NC State News Services
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
As marijuana is becoming legal in more and more states, cases of pets becoming poisoned are on the rise too.
Pieper Veterinary January 13, 2022

As marijuana is becoming legal in more and more states, cases of pets becoming poisoned are on the rise too. Marijuana contains a compound called Tetrahydrocannabinol, more commonly known as THC. When a pet ingests THC it can cause symptoms such as lethargy, vomiting, difficulty walking or stumbling, urinary incontinence, and trembling or crying. In severe cases it can cause an erratic heart rate and even seizures. Toxicity is usually not fatal, but supportive care such as fluids and medications are needed to help keep your pet healthy and comfortable while they recover.
Pets can be exposed to THC in many ways, but it’s most commonly seen with dogs who eat their owner’s marijuana edibles such as brownies and butter. Buds and second-hand smoke can also be a risk. It’s very important to keep anything in your house that contains marijuana secure and out of reach of any pets. If your pet does ingest marijuana or is displaying symptoms of toxicity, please contact ASPCA poison control or an emergency vet immediately.

Page 10 previous page next page